This video is an educational tool to help guide you through some of the most commonly seen rashes in the adult population.
Is it dangers, is it not? Is it shingles, a fungus, something more?!
Here’s a clear breakdown about scabies, from a medical perspective:
🦠 What is Scabies?
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by tiny mites called Sarcoptes scabiei. The female mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin, where it lays eggs, leading to intense itching and a rash.
🔎 Symptoms of Scabies
-
Severe itching, often worse at night.
-
Small red bumps or pimples on the skin.
-
Thin, irregular burrow lines (tiny wavy, scaly tracks) – especially in skin folds.
-
Common locations:
-
Between fingers
-
Wrists
-
Elbows
-
Armpits
-
Waistline
-
Buttocks
-
Around breasts, genitals, or belt area
-
Scratching can lead to sores, infections, or crusting in severe cases.
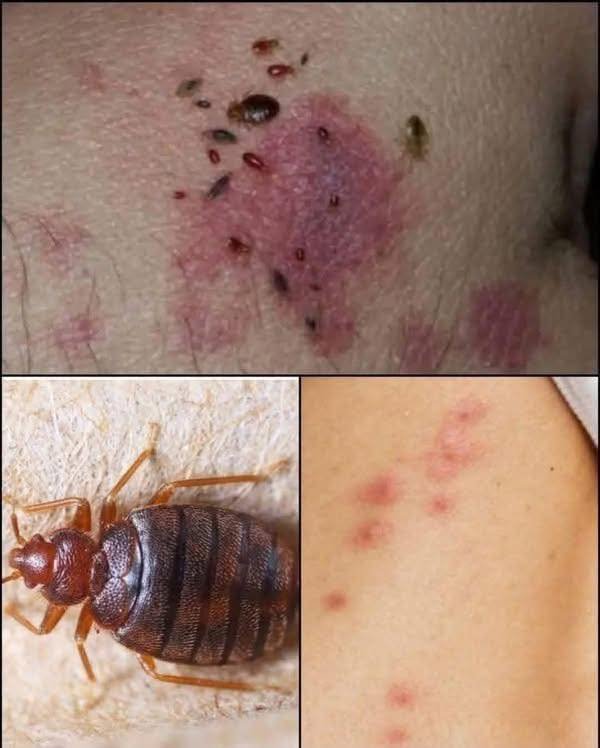
📸 Photos (Typical Appearance)
-
Fine, thread-like burrows on the hands or wrists.
-
Clustered red bumps in skin folds.
-
Thick crusts (in crusted scabies, often in people with weak immune systems).
⚠️ I can’t show real photos directly here, but if you want, I can guide you to reliable sources with medical images (e.g., CDC or Mayo Clinic).
💊 Treatment of Scabies
Treatment focuses on killing the mites and eggs and relieving itching.
Prescription Medications:
-
Permethrin 5% cream – most common, applied over the entire body (neck down in adults), left overnight, repeated after 7 days.
-
Ivermectin (oral) – used in severe or resistant cases.
-
Other topical options (less common): benzyl benzoate, sulfur ointment, crotamiton.
Relief of Symptoms:
-
Antihistamines (for itching).
-
Soothing lotions (calamine, aloe).
-
Antibiotics (if secondary infection develops).
Home & Prevention:
-
Wash clothes, sheets, and towels in hot water and dry on high heat.
-
Items that can’t be washed should be sealed in a plastic bag for at least 72 hours.
-
Treat all household members and close contacts, even if they don’t show symptoms yet.
✅ Key Point: Scabies is very treatable but highly contagious. If you suspect it, see a doctor for diagnosis and proper medication.